
Common ACL Injuries in Athletes Treated Through Arthroscopy
Common ACL Injuries in Athletes Treated Through Arthroscopy
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) injuries are among the most prevalent and debilitating injuries faced by athletes across a range of sports. Whether it’s a football player pivoting on the field, a basketball player making a sharp cut, or a skier landing a jump, the ACL often absorbs the force from high-impact movements. Thanks to advancements in medical technology, particularly arthroscopic surgery, the treatment of ACL injuries has evolved significantly, allowing athletes to recover more quickly and achieve better outcomes.
This article explores how arthroscopy effectively addresses common ACL injuries in athletes, outlines symptoms, discusses treatment options, and provides recovery insights from sports injury experts.
What Is an ACL Injury?
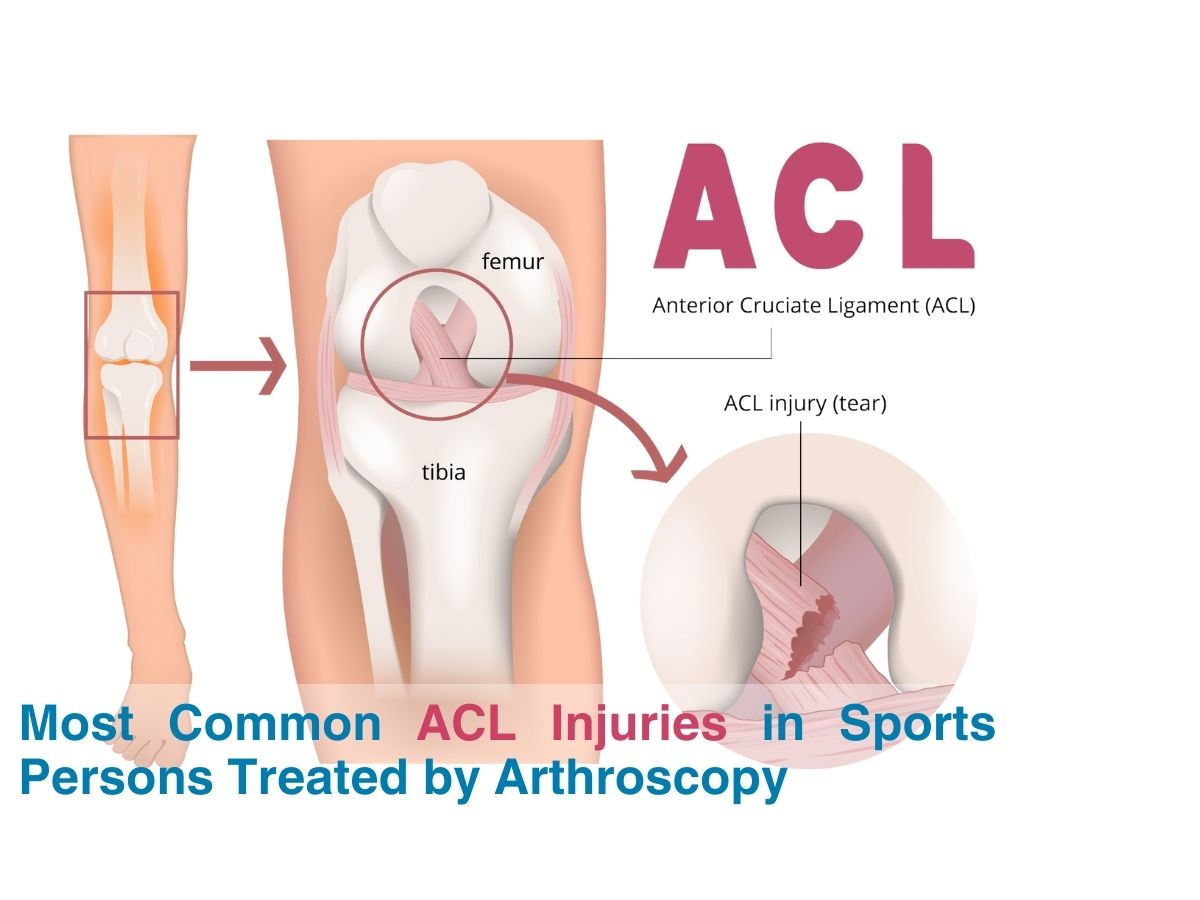
The ACL is one of the four primary ligaments in the knee that connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). It plays a crucial role in stabilizing the knee, particularly during activities involving sudden stops, changes in direction, or jumping. ACL injuries typically occur when the ligament is overstretched or torn, often as a result of intense physical activity or sports.
Common Types of ACL Injuries in Athletes
- Partial Tear of the ACL:
A partial tear occurs when some fibers of the ACL are damaged, but the ligament is not completely severed. Athletes with a partial tear may experience knee instability and discomfort, but the ligament remains intact to some degree. - Complete Tear of the ACL:
A complete tear happens when the ACL is fully torn, resulting in significant knee instability. This is one of the most common ACL injuries in athletes and typically requires surgical intervention. - ACL Sprain:
An ACL sprain occurs when the ligament is overstretched but not torn. Sprains are classified into three grades:
- Grade 1: Minor stretch with no tearing.
- Grade 2: Partial tear of the ligament.
- Grade 3: Complete tear of the ligament.
- Associated Meniscal Tears:
Many ACL injuries occur in conjunction with meniscal tears, which involve damage to the cartilage that cushions the knee joint. These combined injuries often require specialized surgical treatment. - ACL Avulsion Fracture:
In rare cases, the ACL may cause a small piece of bone to tear away where the ligament attaches to the tibia. This injury is more common in younger athletes.
How Arthroscopy Helps Treat ACL Injuries
Arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments to diagnose and treat knee injuries. In the case of ACL injuries, arthroscopy allows surgeons to repair or reconstruct the ligament with minimal disruption to surrounding tissues. Here’s how it works:
- Diagnosis and Assessment:
Arthroscopy allows the surgeon to assess the severity of the ACL injury in real time and check for any associated damage to the meniscus, cartilage, or other ligaments. - Reconstruction Surgery:
For complete ACL tears, reconstruction surgery is often necessary. This involves replacing the damaged ligament with a graft, typically taken from the patient’s own hamstring or patellar tendon, or from a donor tissue. - Precision and Faster Recovery:
Because arthroscopy involves smaller incisions, it leads to less trauma to the knee. This results in reduced recovery times and less postoperative pain for athletes.
Benefits of Arthroscopy for ACL Injuries
- Minimally Invasive: Smaller incisions mean less scarring and quicker healing.
- High Accuracy: Advanced imaging technology ensures precise diagnosis and treatment.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Athletes can often return to their sport sooner than with traditional open surgery.
- Lower Risk of Complications: The risk of infection is reduced, and patients experience better long-term outcomes.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-surgery recovery typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and gradual return to physical activity. Athletes can often resume low-impact activities within 3-6 months and return to competitive sports within 9-12 months, depending on the severity of the injury and adherence to the rehabilitation plan.
While ACL injuries present a significant challenge for athletes, arthroscopic surgery has made treatment more effective and recovery much faster. Thanks to the expertise of orthopedic surgeons, athletes can regain their mobility and return to their sport with confidence. Whether dealing with a partial tear, a complete rupture, or an associated injury, arthroscopy offers a precise, minimally invasive solution with excellent long-term outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of an ACL injury?
Typical symptoms include a “popping” sensation in the knee, immediate swelling, pain, instability, and difficulty bearing weight on the affected leg.
How is an ACL injury diagnosed?
An ACL injury is diagnosed through physical examination, imaging tests such as MRI, and in some cases, arthroscopy for a more detailed assessment.
Is arthroscopy the only treatment option for ACL injuries?
Not all ACL injuries require surgery. Minor sprains or partial tears may heal with rest, bracing, and physical therapy. However, for complete tears, arthroscopic surgery is often the best treatment option for athletes.
How long does it take to recover from arthroscopic ACL surgery?
Recovery typically takes 6-12 months, depending on the injury’s severity, the surgical procedure, and the rehabilitation process.
Can athletes return to their sport after ACL reconstruction?
Yes, most athletes can return to their sport after completing rehabilitation. A structured rehab plan is essential for optimal recovery.
What are the risks of arthroscopic ACL surgery?
Although arthroscopy is generally safe, potential risks include infection, stiffness, or graft failure. These risks are minimized when proper surgical techniques and post-operative care are followed.

Dr. Kushal Hippalgaonkar
MBBS, DNB (Orthopaedics)
Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon






