
How Does Bad Cholesterol Affect Blood Flow to the Heart?
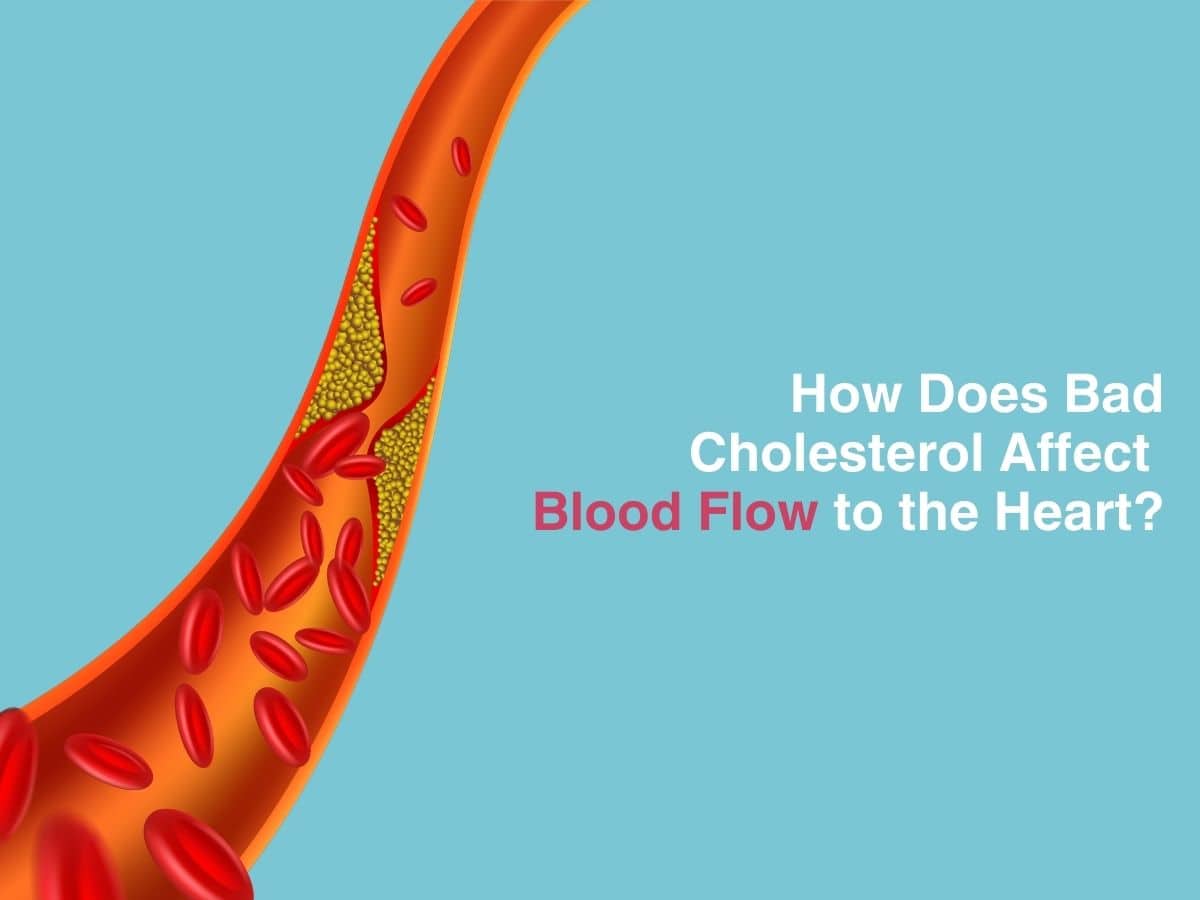
Introduction- We have all heard of the terms ‘bad cholesterol’ and ‘good cholesterol’ being thrown around a lot, in the context of heart disease. This waxy, fatty compound has been a villain for so long, most of us don’t even know that it is a normal compound that our body synthesises. The quantity in which it is made and stored is what is important. This compound is an important ‘sterol’ that our organs prefer to use as a fuel source.
The Relationship Between Cholesterol Levels And Cardiovascular Health
Cholesterol helps make cellular membranes stable, is a crucial part of many hormones in our body and helps your skin cells make Vitamin D. Cholesterol is of many kinds- VLDL, LDL and HDL- which stand for very low density lipoprotein, low density lipoprotein and high density lipoproteins respectively. These terms are just another way to describe the size of the molecule. Dietary choices which involve lots of trans fats can cause fatty liver disease, which can increase cholesterol production. Levels of each of these lipoproteins are closely regulated. But increases can cause a gradual build up of obstructive plaques, which can cause high BP and worsen cardiovascular health in the long run. Let us look at some values to reinforce this concept, shall we?
- LDL levels need to be below 100 mg/dl of blood. Any higher and you have a higher chance of suffering from stroke or a heart attack.
- HDL should be below 50 mg/dl of blood.
- You should try to reduce LDL levels and increase HDL levels. Why? HDL can carry cholesterol molecules to the liver, which can then be broken down and flushed from the body and does not form plaques. Too much LDL can mean plaque formation.
The Role Of Diet And Lifestyle In Managing Bad Cholesterol
Your dietary choices matter a lot when it comes to ascertaining your risk for heart disease. You should try not to eat highly processed or fatty foods and instead focus on including fresh produce in multiple servings every day. Keeping track of food alone is not enough, you will also need to add in some exercise and a de- stressing regimen of some sort. Most of these metabolic disorders have a lifestyle basis to them and making changes to your daily routine can greatly reduce that risk by a lot.
Medications That Help Reduce Bad Cholesterol And Prevent Heart Disease
Treating cholesterolemia is done in a few different ways. Some of them may focus on helping your vascular system work better while others try to reduce cholesterol levels themselves. The treatment regimen chosen depends on your blood cholesterol and triglyceride values. High cholesterol is a systemic problem because the plaque can mean reduced blood supply to a particular area. Cut off blood flow to the brain and you have a stroke, to the heart and you have a heart attack while a blockage in your limbs can cause peripheral artery disease.
The Importance Of Regular Cholesterol Screenings For Heart Health
Monitoring blood cholesterol levels is the only way you can stay on top of them and work systematically to keep them in control. This is a very general screening or testing schedule we have for you, but please remember to talk to your doctor if you have any other concerns.
Ages 19 and below
- Kids aged between 9-11 should ideally get tested.
- Get kids tested every 5 years.
- If there is a well known family history of heart disease, stroke or cholesterolemia, then kids may be tested when they turn 2 years of age.
For adults 20-65 years of age
- Get tested every 5 years
- Get tested every couple years or annually, once you hit the 45 mark (for men) and 55 mark (for women).
Older than 65
- Get tested annually. No excuses!
- Your doctor may ask you to get tested more often if you have comorbid conditions like diabetes, you are overweight or obese, have high BP issues and are a smoker.
Conclusion
The relationship between cholesterol levels and cardiovascular health is often not explained well. There is a lot of misinformation doing the rounds. We hope we have helped you understand how cholesterol levels make a difference, along with the type involved (HDL is good, LDL is bad). Since these are all disorders that arise from poor lifestyle choices, we think changing your routine can greatly help reduce risk and improve quality of life in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is LDL cholesterol, and why is it considered bad for the heart?
What are the early signs of cholesterol-related heart problems?
What foods increase bad cholesterol levels in the body?
Does high cholesterol always lead to heart disease?
Can lifestyle changes reverse cholesterol-related artery blockages?

Dr. Akash Shastry
MBBS, MD (DNB) Cardiology
PG – Cardiology






